
Infusion tech – history
Vacuum resin infusion is considered a relatively recent process; it was filed in 1959 in U.S. for the production of swimming pools made in fiberglass (GRP, Glass Reinforced Plastic), using a system of distribution of the resin. In the early 80’s Lotus Cars used a similar process for the production of car body parts. In the same years, one of the first applications in the water was a series of RORC One Design yachts, produced by Jeremy Rogers in Lymington, England.
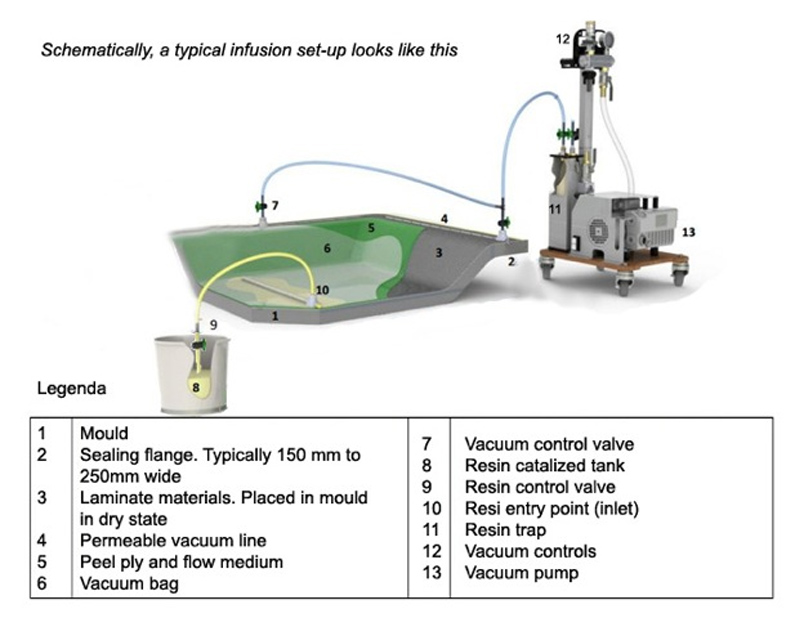
Main aspects of infusion:
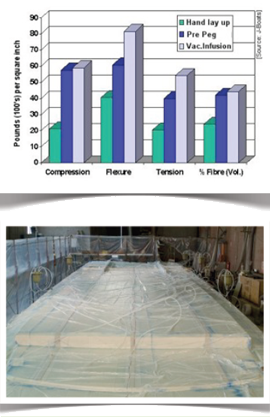
Achievements of vacuum resin infusion
 Process with low emissions of styrene and acetone
Process with low emissions of styrene and acetone Standardized and repeatable process and pieces
Standardized and repeatable process and pieces Excellent composite’s mechanical characteristics
Excellent composite’s mechanical characteristics Weight reduction
Weight reduction Time and costs reduction
Time and costs reduction
Infused Composite’s Quality
Excellent resin / fiber ratio (35%-65%)
Constant thickness
No use of putty or bonder for fixing the core
Absence of interlaminar air bubbles
Excellent mechanical properties of the laminate due to uniform compression exerted by vacuum.
Environment
 Low emissions of styrene in the air
Low emissions of styrene in the air Cleanliness
Cleanliness Reduced costs for PPE and flue gas treatment equipment
Reduced costs for PPE and flue gas treatment equipment
 Ergonomics
Ergonomics No contact with resin by workers
No contact with resin by workers Reductions occupational diseases (carpal tunnel, etc …..)
Reductions occupational diseases (carpal tunnel, etc …..)

Comparison with the main processes:
Attention: The internal data of table “2” is corrupted!
